Manage maternity protection and parental leave easily and in compliance with the law

New contributions:
Experience the future of corporate management: let your employees manage their own data with Employee Self Service!
Why is trust-based working time so controversial? In this blog, we will tell you what trust-based working hours really mean, what opportunities and risks they entail and which legal regulations employees and employers must observe.
Trust-based working hours: flexibility or control and transparency through time tracking?
Why is trust-based working time so controversial? In this blog, we will tell you what trust-based working hours really mean, what opportunities and risks they entail and which legal regulations employees and employers must observe.
Employees with children are particularly protected by law. During pregnancy, women are entitled to maternity protection and therefore also protection against dismissal and redundancy. Furthermore, employment restrictions and bans apply.
In this blog post, we will briefly and concisely explain the two terms Maternity protection and Parental leave closer. And show you how the resulting personnel and absence management can be managed easily and clearly in HR software.
Maternity protection
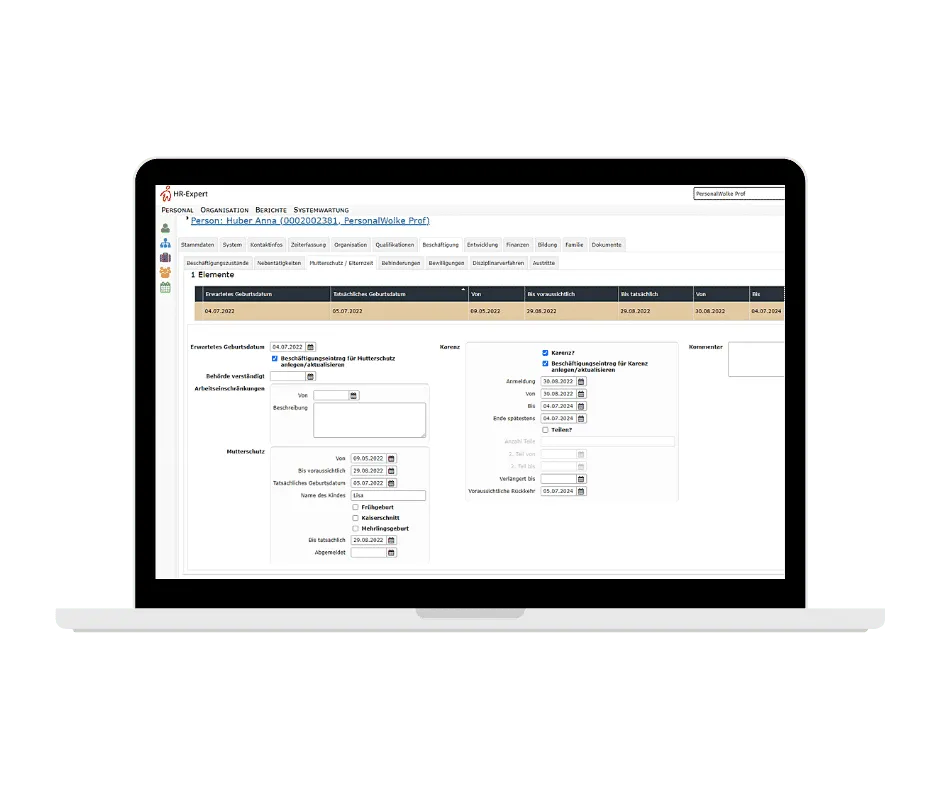
The so-called Maternity protection (employment ban = protection period) applies eight weeks before to eight weeks after the delivery date. In the case of premature, multiple or caesarean births, the period is extended to twelve weeks.
Parental leave
As a mother or father, you are entitled to Parental leave. This begins after the end of the maternity protection period (usually eight weeks after the birth) and ends after the notified (=agreed) duration, but no later than the day before the child's second birthday. If parental leave is to be extended, this requires a written agreement with the employer, including a waiver of the right of termination.
Legal basis and implementation in the personnel cloud
In the Maternity Protection Act 1979 (MSChG) regulates provisions such as a ban on employment, protection against dismissal for pregnant women, maternity pay and continued payment of wages. For fathers, the Paternity Leave Act (VKG) provides for regulations regarding parental leave and part-time work.
According to the MSchG, employers must ensure that the health of expectant and breastfeeding mothers and the protection of children is guaranteed.
This includes reporting obligations to the labor inspectorate, compliance with employment bans and restrictions, protection against dismissal and redundancy, as well as the calculation of remaining leave. The latter is automatically aliquoted with our software when the leave is taken.
In addition, Personalwolke calculates by entering the planned date of birth of the child the beginning and end of maternity leave automatically. If the actual date of birth is then entered and supplemented by special features, e.g. premature birth, caesarean section, multiple birth, etc., the system calculates the maternity protection again automatically: premature birth, caesarean section, multiple birth, the system calculates the maternity protection again automatically. If maternity leave is also taken, the entitlement is also calculated automatically depending on the date of birth. Country-specific laws and regulations (e.g. Germany and Switzerland) can also be easily stored.
Our tip for HR experts
The use of personnel cloud modules is particularly efficient Personnel administration and Time tracking software.
If these two modules are used in combination, the absences resulting from maternity leave and parental leave are transferred to the time management system. The time-consuming and complicated remaining leave allocation is also taken over by Personalwolke.
Benefit from automation and efficient HR processes.
Would you like to find out more about personnel and absence management with Personnel Cloud?
Arrange a free consultation now and we will get back to you shortly.